”Four nuclear waste containers depressurized at Los Alamos, raising fresh questions about safety at one of America’s most closely watched laboratories.”
Nuclear safety is something most of us rarely think about in our daily lives—until a headline reminds us why it matters. That moment came recently when officials at Los Alamos National Laboratory confirmed that four nuclear waste containers had depressurized, raising new questions about oversight and safety at one of the most significant nuclear research facilities in the United States.

While authorities say there’s no immediate danger to the public, the incident has sparked unease. After all, when it comes to nuclear waste management, even a small slip can carry big implications. From scientific mishaps to human error, the Los Alamos case highlights how fragile and complex nuclear safety truly is.
So what exactly happened, and what does it mean for the community, the environment, and the future of nuclear safety? Let’s break it down.
What Happened at Los Alamos?
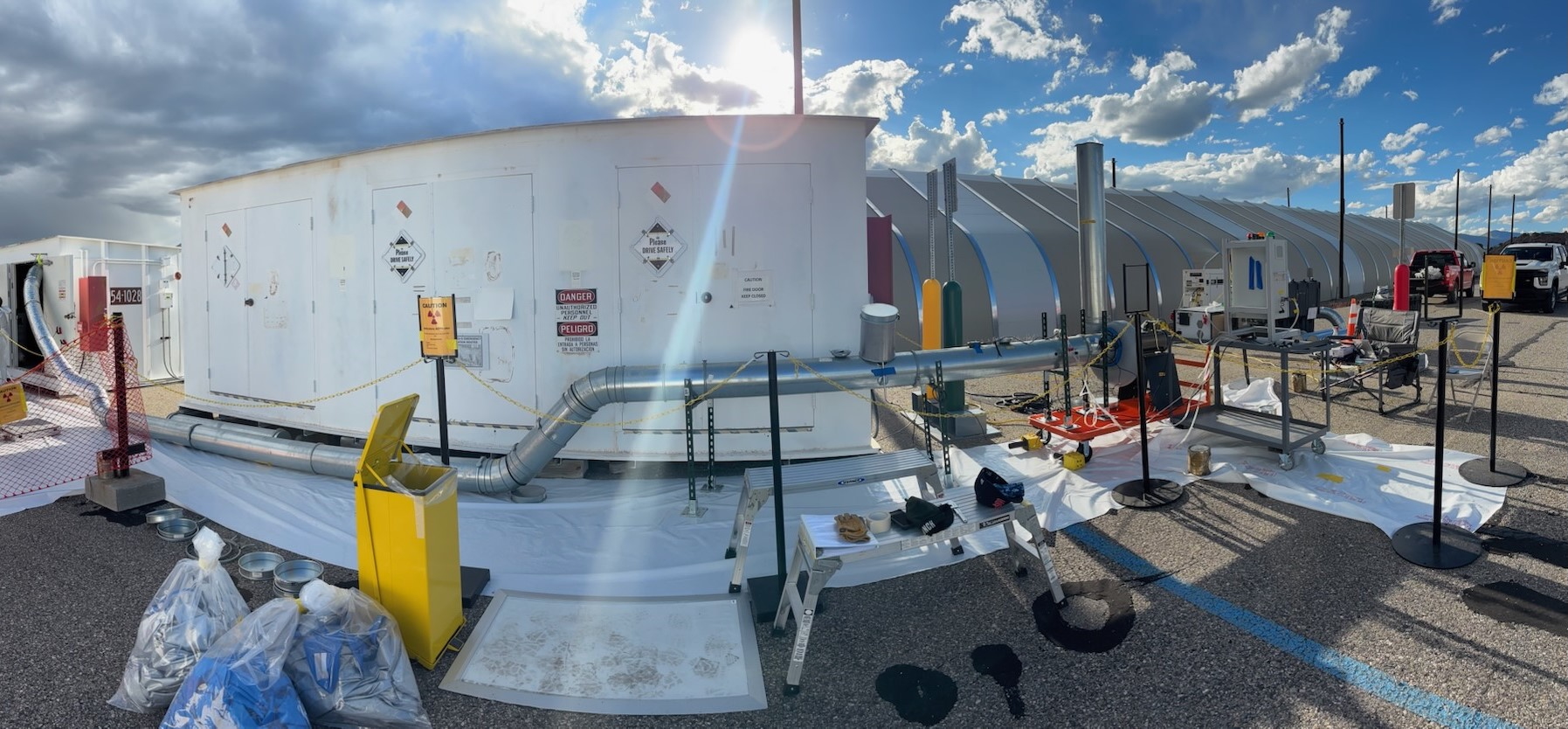
The incident at Los Alamos National Laboratory began when workers discovered that four containers holding nuclear waste had depressurized. In simple terms, the airtight seal inside the containers was compromised, creating concern over whether dangerous materials could escape.
Officials quickly confirmed that the containers were stored in a controlled environment and that there was no immediate risk to the public. Still, the discovery raised alarms because Los Alamos is no ordinary facility—it’s one of the most important nuclear research and weapons labs in the United States, with a long history tied to nuclear safety.
At this stage, investigators are still trying to determine exactly why the containers depressurized. Whether it was a chemical reaction inside the waste, an error in packaging, or a flaw in the storage system, the fact that multiple containers failed at once has made experts take the situation very seriously.
For the lab, the incident is more than just a technical problem—it’s a reminder that nuclear waste management requires constant vigilance. And for the public, it’s a headline that naturally sparks concern: if it can happen here, where else might it happen?
What Happened at Los Alamos?
The incident at Los Alamos National Laboratory began when workers discovered that four containers holding nuclear waste had depressurized. In simple terms, the airtight seal inside the containers was compromised, creating concern over whether dangerous materials could escape.
Officials quickly confirmed that the containers were stored in a controlled environment and that there was no immediate risk to the public. Still, the discovery raised alarms because Los Alamos is no ordinary facility—it’s one of the most important nuclear research and weapons labs in the United States, with a long history tied to nuclear safety.
At this stage, investigators are still trying to determine exactly why the containers depressurized. Whether it was a chemical reaction inside the waste, an error in packaging, or a flaw in the storage system, the fact that multiple containers failed at once has made experts take the situation very seriously.
For the lab, the incident is more than just a technical problem—it’s a reminder that nuclear waste management requires constant vigilance. And for the public, it’s a headline that naturally sparks concern: if it can happen here, where else might it happen?
Why Depressurization Is a Concern
At first glance, the term “depressurization” might sound like a minor technical issue, but when it comes to nuclear waste, it’s anything but. These containers are specifically designed to hold hazardous materials under tightly sealed conditions. If that seal is broken, the safety barrier between radioactive waste and the outside world becomes less reliable.
Even though officials at Los Alamos have reassured the public that there’s no immediate radiation leak, the incident sparks concern because depressurization could signal deeper problems. It may point to chemical reactions inside the waste, flaws in the way the containers were built, or issues in how they were handled or stored. Any of these factors could raise the risk of dangerous leaks if not addressed quickly.
The bigger worry is trust. Nuclear waste is expected to remain hazardous for decades—even centuries. If containers can’t reliably hold up now, people naturally wonder what could happen years down the road. For the surrounding community, the news is unsettling. For scientists and regulators, it’s a wake-up call to dig deeper into what went wrong and ensure it doesn’t happen again.
When it comes to nuclear safety, small lapses can have big consequences, and that’s why depressurization is treated with such urgency.
Official Response and Safety Measures
When word got out that four nuclear waste containers had depressurized, it naturally stirred concern. In response, Los Alamos National Laboratory was quick to calm fears, reassuring people that the containers were stored in a secure area and that no one in the community was in immediate danger.
But reassurance wasn’t enough on its own. The lab immediately sent in safety teams to check the containers, monitor the area, and make sure nothing harmful had leaked. At the same time, investigators started digging into the bigger question: what went wrong? Was it a flaw in the containers, a chemical reaction inside, or a mistake in handling?
To address those concerns, Los Alamos has promised to tighten safety checks and review how waste is handled, while also working with federal agencies to prevent similar issues from slipping through in the future. The message was clear—they want to restore trust and show the community that protecting people comes before anything else.
Incidents like this remind us that with nuclear materials, even a small slip can feel like a big scare. And while the lab’s quick response may offer some comfort, many will be watching closely to see not just what officials say, but how they follow through.
The Bigger Picture: Nuclear Waste Management Challenges
The Los Alamos incident is more than a one-off problem—it’s a reminder of just how complicated nuclear waste management really is. Every container, every storage site, and every safety protocol has to work perfectly, not just for today but for decades, even centuries. That’s a huge responsibility, and it’s one that governments and scientists around the world continue to struggle with.
Unlike other types of waste, nuclear materials don’t just “go away.” They remain hazardous for generations, meaning storage solutions must be built to last longer than most of us can even imagine. And while technology has come a long way, the Los Alamos case shows that even the best systems can face unexpected challenges—whether it’s chemical reactions, container flaws, or human error.
There’s also the question of public trust. When people hear about failures at a high-security lab, it’s natural for them to wonder: if this can happen here, what about other sites? Transparency, accountability, and stronger safety measures aren’t just technical requirements—they’re essential for keeping communities confident that they’re protected.
The bigger picture is clear: safe nuclear waste storage is not simply a scientific challenge, but a human one. It’s about ensuring that the energy choices we make today don’t put future generations at risk. Incidents like Los Alamos remind us that vigilance isn’t optional—it’s the price of managing something as powerful, and as dangerous, as nuclear material.
FAQs
1. What exactly happened at Los Alamos National Laboratory?
Officials reported that four containers holding nuclear waste depressurized, meaning their seals were compromised. While the containers were stored in a secure facility, the discovery raised concerns about safety and long-term storage practices.
2. Was there any danger to the public?
According to Los Alamos officials, there was no immediate risk to workers or the surrounding community. The containers were in a controlled area, and monitoring showed no evidence of radiation release. Still, the incident is being taken seriously.
3. Why is depressurization a big deal?
Nuclear waste containers are designed to remain tightly sealed to keep hazardous materials secure. When they lose pressure, it raises questions about whether the waste inside could react, leak, or cause problems down the line.
4. Has Los Alamos faced similar issues before?
Yes, Los Alamos has had past challenges related to nuclear waste handling. While safety measures have improved over the years, the lab remains under close watch because of its history and its critical role in U.S. nuclear research.
5. What steps are being taken to fix the problem?
The lab has launched an investigation to find out what went wrong. In the meantime, it has promised tighter safety checks, closer monitoring of containers, and stronger oversight from federal agencies to prevent similar issues in the future.
6. What does this mean for nuclear waste management overall?
This incident highlights the broader challenge of storing nuclear waste safely for the long term. Even in a top research facility, unexpected problems can occur. It’s a reminder that vigilance, transparency, and constant improvements are essential to keep people safe.